Introduction
The field of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) relies heavily on a dedicated workforce to provide high-quality services to individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities. Registered Behavior Technicians (RBTs) are at the forefront of this service delivery, working directly with clients to implement treatment plans. However, the ABA industry is facing a significant challenge: an exceptionally high turnover rate among RBTs. This report explores the latest data on RBT turnover, its impact on the industry, and the key factors contributing to this critical issue.
The Scale of the Problem: RBT Turnover Statistics
Recent data paints a stark picture of the RBT turnover crisis. According to the CentralReach 2025 Autism and IDD Care Market Report, ABA organizations experienced average turnover rates between 77.4% and 103.3% in 2024 1
The size of the organization appears to be a significant factor, with larger organizations facing the highest turnover rates.
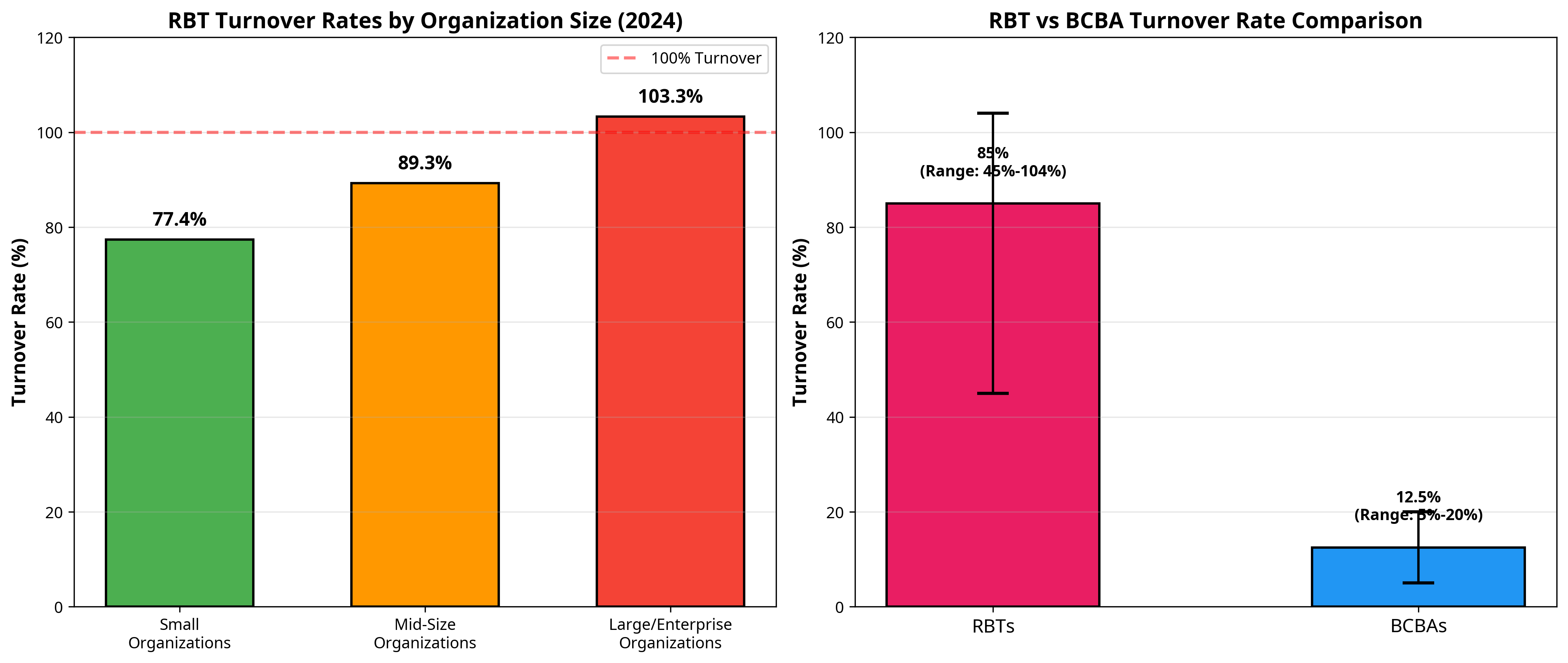
Figure 1: RBT turnover rates in 2024, broken down by organization size. Data from the CentralReach 2025 report shows a clear trend of increasing turnover with larger organizational size.
This high turnover is not a new phenomenon, but it has been exacerbated in recent years. While the RBT workforce has grown substantially, from approximately 70,000 in 2020 to nearly 200,000 by 2024, much of this growth is attributed to backfilling positions rather than a net increase in the workforce 2
In 2024 alone, over 30,000 RBTs left the field, highlighting the severity of the retention problem.
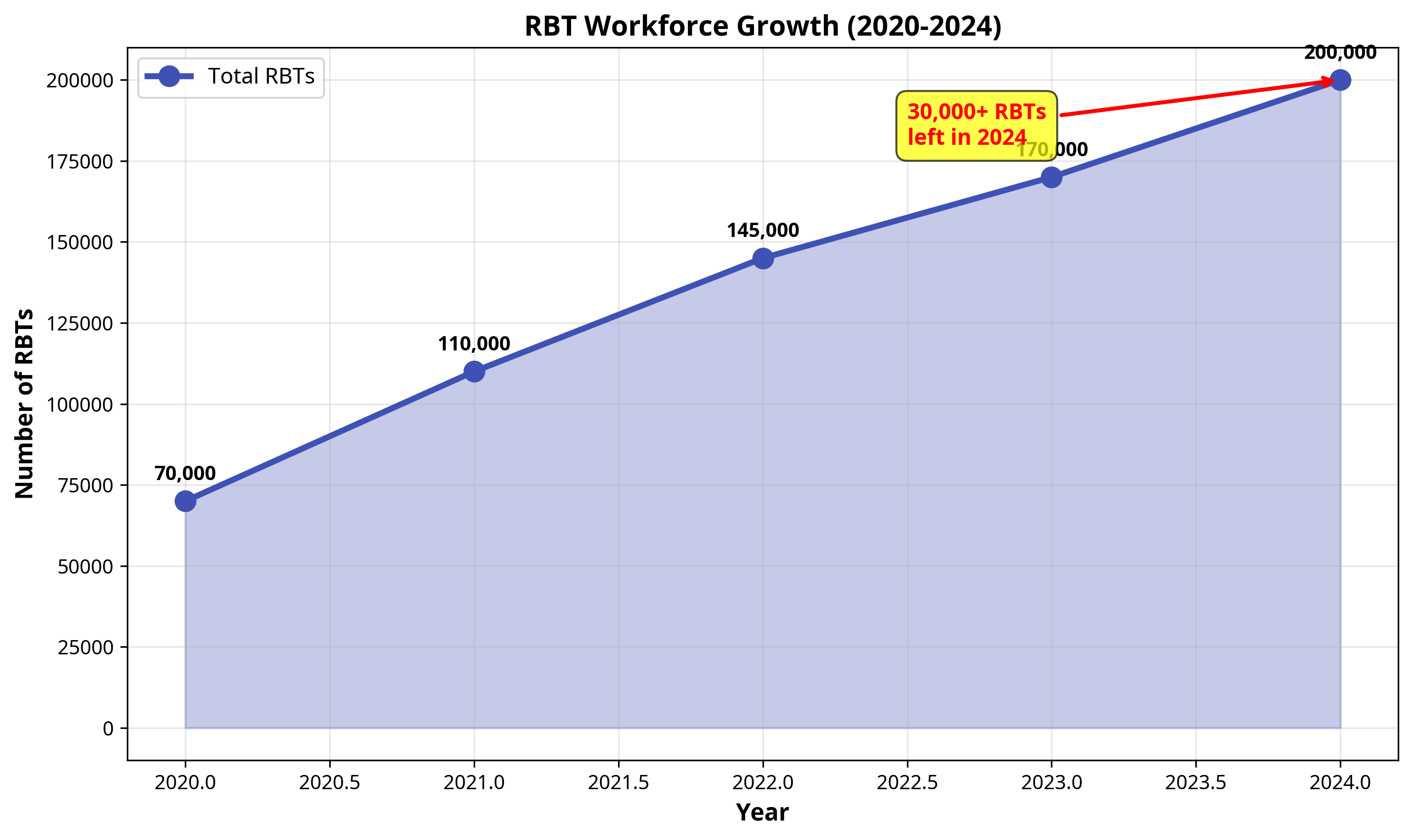
Figure 2: The growth of the RBT workforce from 2020 to 2024. Despite the increase in numbers, the high turnover rate indicates a revolving door of talent.
In stark contrast, the turnover rate for Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) is significantly lower, ranging from 5% to 20% annually.
This disparity underscores the unique challenges faced by RBTs in the field.
Key Factors Driving RBT Turnover
A combination of factors contributes to the high rate of RBT turnover. These issues often lead to burnout, dissatisfaction, and the decision to leave the field.
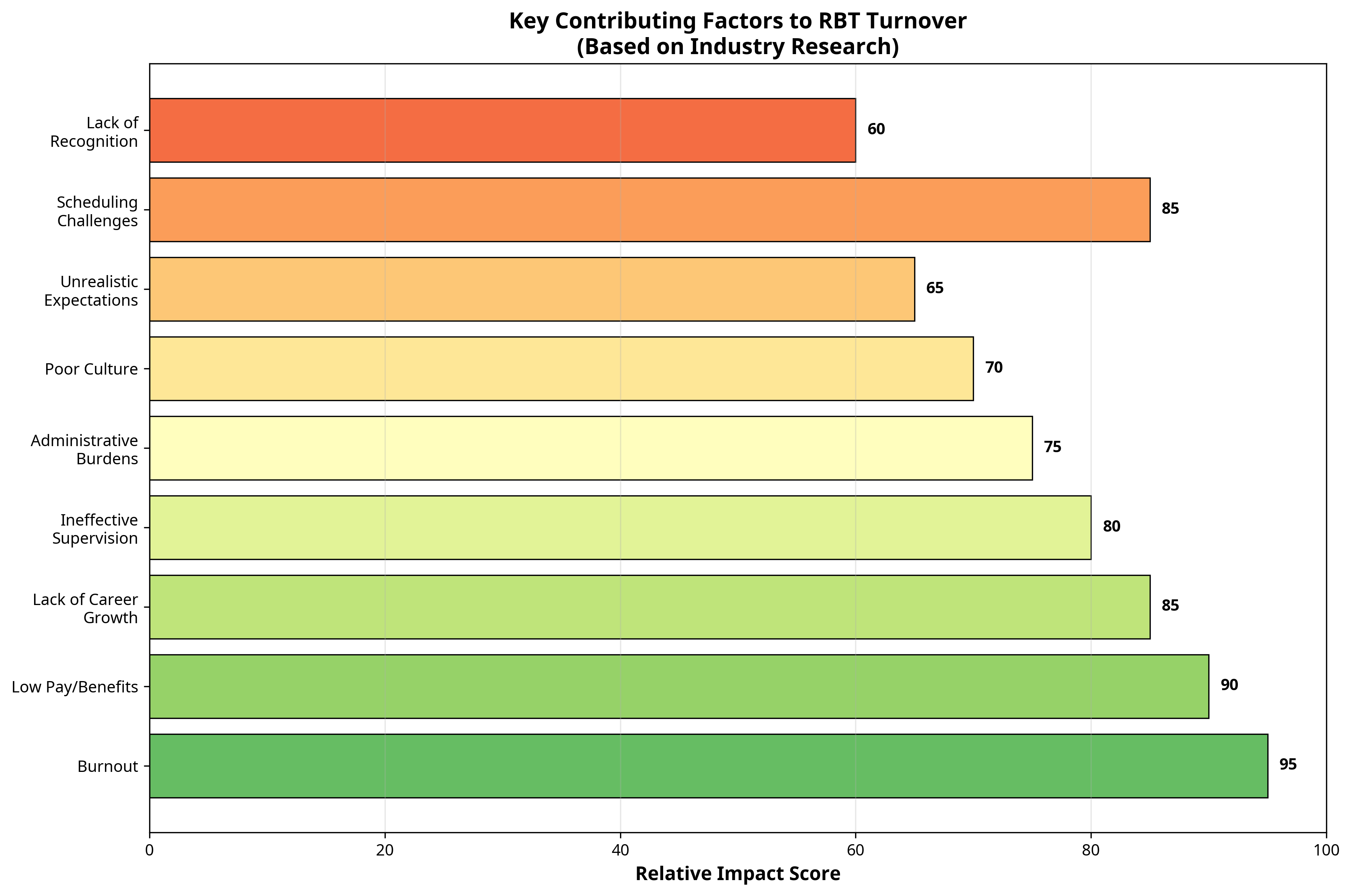
Figure 3: An analysis of the key factors contributing to RBT turnover, based on industry research. Burnout, low pay, and lack of career growth are among the most significant drivers.
The most commonly cited reasons for RBT turnover include:
- Burnout: High caseloads, emotional exhaustion from working with challenging behaviors, and a lack of work-life balance are major contributors to burnout.
- Low Pay and Lack of Benefits: Compensation often does not reflect the demanding nature of the job, and many RBTs lack access to comprehensive benefits packages.
- Lack of Career Growth: Many RBTs see limited opportunities for advancement within their organizations, leading them to seek careers with more potential for growth.
- Ineffective Supervision and Support: A lack of adequate supervision, mentorship, and support from BCBAs and management can leave RBTs feeling isolated and ill-equipped to handle the challenges of their roles.
- Administrative Burdens: Excessive paperwork, inefficient workflows, and complex documentation requirements can detract from the time RBTs spend with clients.
The Impact of High Turnover
The consequences of high RBT turnover are far-reaching, affecting not only the organizations themselves but also the clients they serve. The constant churn of staff can lead to:
- Decreased Quality of Care: Inconsistent service delivery and a lack of continuity can negatively impact client progress.
- Increased Operational Costs: The costs associated with recruitment, hiring, and training new RBTs are substantial.
- Negative Impact on Staff Morale: High turnover can create a stressful and unstable work environment for the remaining staff.
- Damage to Organizational Reputation: A reputation for high turnover can make it difficult to attract and retain qualified staff.
Conclusion
The high turnover rate among Registered Behavior Technicians is a critical issue that threatens the stability and quality of ABA services. Addressing this challenge requires a multi-faceted approach that focuses on improving compensation and benefits, providing clear pathways for career advancement, fostering a supportive and positive work environment, and ensuring that RBTs receive the high-quality supervision and training they need to succeed. By investing in their RBT workforce, ABA organizations can not only improve retention but also enhance the quality of care they provide to their clients.
References
[1] ABA Resource Center. (2025). Breaking the Cycle: Addressing High RBT & BCBA Turnover in ABA.
[2] LinkedIn. (2025). How Peer-to-Peer Recruiting Can Solve ABA's Workforce Crisis.
[4] Forbes. (2018). Improving Retention in ABA Services.
[5] BHCOE. (2025). Why RBTs Leave... and What We Can Do to Keep Them.